Tooth decay begins when bacteria in your mouth makes acid that attacks the tooth surface (enamel) leading to small to big holes in the tooth called cavity. If left untreated, it leads to pain, infection or even tooth loss. The stages of tooth decay are:-
- DEMINERALISATION:-
The first stage of tooth decay is caused when a tooth is exposed to significant amounts of acid produced by plaque bacteria. When teeth aren’t brushed and plaque is allowed to sit on teeth, they will slowly begin to lose the minerals that make up their enamel. Stage 1 tooth decay can be detected by looking for small white spots on teeth, which indicate a loss of minerals and enamel. This condition can be reversed by remineralization.
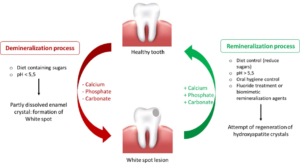
- ENAMEL DECAY
The second stage of tooth decay involves the further break down of tooth enamel. People who have developed white spots due to mineral loss will notice them turning a brownish color, which indicates even greater loss of minerals and enamel. Stage 2 decay puts people at much higher risk of developing cavities. Fluoride treatment and restorations are done to treat these defects.
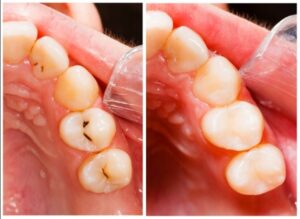
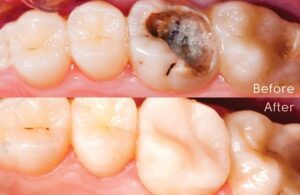
- DENTINE DECAY
Beneath tooth enamel is a tissue called dentin. When enamel wears down, it exposes dentin to decay. Because dentin is softer than enamel, it’s more sensitive to the effects of acid produced by plaque bacteria, and that means it decays faster than enamel. Restorations are done to save these tooth defects.
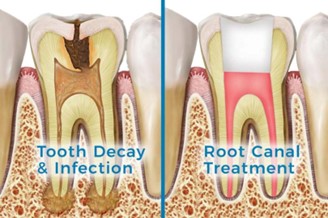
- PULP DAMAGE AND ABCESS
When dentin begins to fully decay, it exposes pulp, which is the innermost part of a tooth. Nerves and blood vessels are located in the pulp. When decay begins to affect pulp, people can experience irritation and swelling, increased sensitivity, and pain. When pulp becomes heavily damaged, bacteria can spread and multiply inside the tooth near blood vessels and nerves. This can result in significant inflammation and a pocket of pus near the bottom of the tooth called an abscess. Tooth abscesses result in severe pain that can spread into the jaw, and they require immediate treatment involving antibiotics, root canal treatment or tooth extraction depending upon condition of the tooth.